Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

No time to read?
Click below to listen to our podcast on Data Stewardship
In today’s data-driven world, the importance of effective data governance cannot be overstated. But did you know that over two thirds of organizations struggle to implement successful data governance strategies?
Enter data stewardship – the unsung hero of modern data management!
In this article, I’m going to dive deep into the critical role of data stewardship in shaping robust data governance frameworks.
From ensuring data quality to navigating complex compliance landscapes, I’ll explore how data stewards are the key to unlocking the true potential of your organization’s most valuable asset – its data.
I think you will find this article really helpful and by the end you will have a clear understanding of what data stewardship is and how it can really make a difference.

First, let’s get our definitions straight. Data stewardship is the practice of ensuring the quality, integrity, and security of an organization’s data assets throughout their lifecycle. It’s like having a dedicated guardian for your data – someone who makes sure it’s accurate, accessible, and used responsibly.
Now, you might be wondering, “How does this fit into data governance?” Well, think of data governance as the overarching framework that sets the rules and policies for how data should be managed. Data stewardship is the hands-on implementation of these policies. It’s where the rubber meets the road in the world of data management.
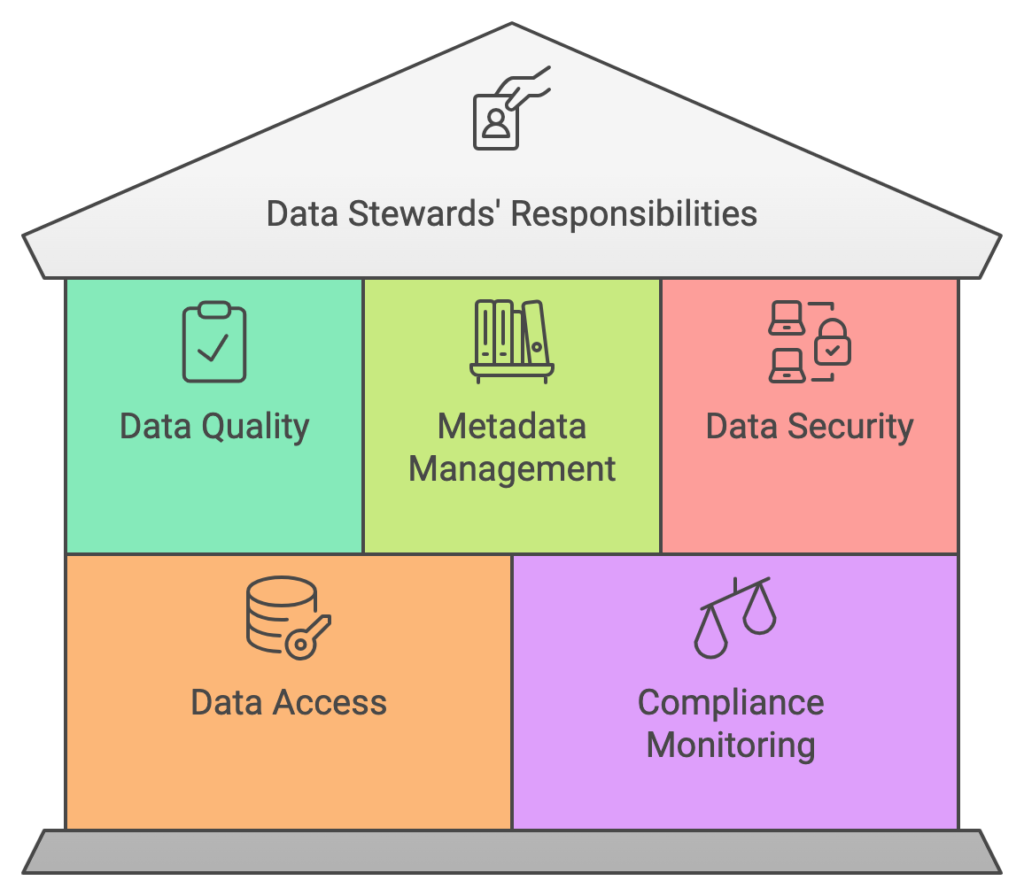
Key Responsibilities of Data Stewards:
Let’s take a quick trip down memory lane. Back in the day, data stewardship was primarily about keeping paper records organized and accessible. Fast forward to today, and oh boy, have things changed! With the explosion of big data, cloud computing, and AI, data stewardship has evolved into a complex, multifaceted discipline.
In 2024, data stewards are grappling with massive volumes of data from diverse sources – everything from IoT devices to social media feeds. They’re not just filing clerks anymore; they’re strategic partners in driving business value through data. As one data expert put it, “Modern data stewards are part librarian, part data scientist, and part business strategist.”
Modern data stewards are part librarian, part data scientist, and part business strategist.
Now that we’ve got the basics down, let’s explore the four key pillars that form the foundation of effective data stewardship. These are the areas where data stewards really earn their stripes!
Picture this: you’re about to make a crucial business decision based on your data, only to find out that the data is incomplete, inaccurate, or outdated. Yikes! This is where data quality management comes in, and it’s a top priority for data stewards.
Data stewards are responsible for:
Pro tip: Automated data profiling tools can be a game-changer in identifying and fixing data quality issues before they snowball into bigger problems.
If data is the new oil, then metadata is the refinery that makes it useful. Metadata provides context and meaning to your data, making it discoverable and understandable. Data stewards play a crucial role in managing metadata and creating comprehensive data catalogs.
Key aspects of metadata management include:
Pro tip: There is a growing number of tools that can be used to support meta data management, data cataloguing and business glossaries. Leave me a message if you want to know more about this!
In an era of increasing data breaches and privacy concerns, data security is more critical than ever. Data stewards work closely with IT security teams to ensure that data is protected from unauthorized access and breaches.
Data Stewards can support:
Opinion: Remember, security isn’t just about keeping the bad guys out – it’s also about ensuring that the right people have access to the data they need when they need it.
Data, like all good things, has a lifecycle. From creation to archival or deletion, data stewards oversee the entire journey of data through an organization.
Data Stewards are involved in:
By effectively managing the data lifecycle, data stewards help organizations minimize risks, reduce storage costs, and maintain compliance with data retention regulations.
Let’s talk about compliance – the word that strikes fear into the hearts of many business leaders! But fear not. With effective data stewardship, navigating the complex world of data regulations becomes much more manageable.

The regulatory landscape is constantly evolving, with new data protection laws popping up faster than you can say “privacy policy.” Data stewards play a crucial role in ensuring that organizations stay compliant with regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the US.
Key compliance responsibilities include:
In the age of data breaches and privacy scandals, consumers are more concerned than ever about how their personal information is used. Data stewards are at the forefront of protecting individual privacy by:
How long should you keep data? When should you delete it? These are questions that keep many a data steward up at night. Effective data retention and deletion policies are crucial for both compliance and operational efficiency.
Data stewards work on:
When the auditors come knocking (and they will), data stewards need to be ready. Maintaining comprehensive audit trails and reports is essential for demonstrating compliance.
This involves:

So, we’ve covered the what and why of data stewardship, now let’s talk about the how. Implementing a robust data stewardship program isn’t a walk in the park, but the benefits far outweigh the challenges.
First things first – you need to clearly define what data stewards will do in your organization. This might include:
Remember, data stewardship isn’t just an IT function – it requires collaboration across the entire organization.
There’s no one-size-fits-all approach to structuring a data stewardship team. Some organizations opt for a centralized model, while others prefer a federated approach with data stewards embedded in different business units.
Regardless of the model you choose, consider including these roles:

In 2024, data stewards have a wealth of tools at their disposal to make their jobs easier and more effective. Some key technologies to consider include:
When selecting tools, focus on those that integrate well with your existing systems and provide the functionality you need to support your data stewardship goals.
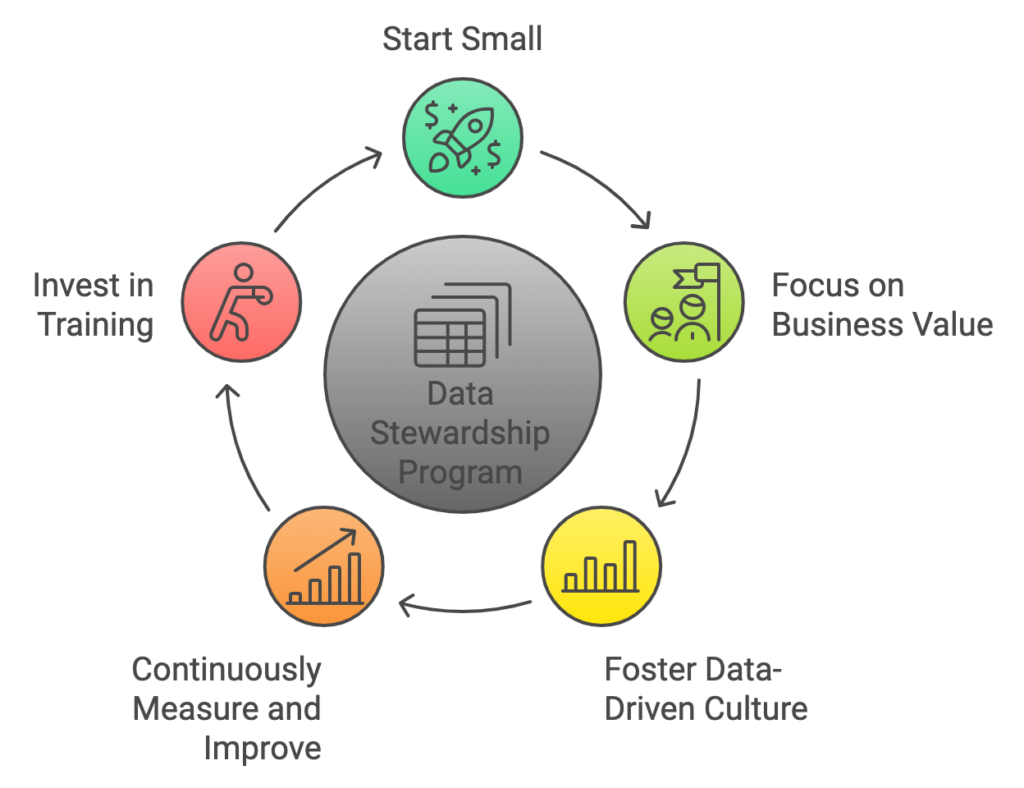
Implementing a data stewardship program is a journey, not a destination. Here are some best practices to guide you along the way:
Let’s face it – implementing data stewardship isn’t all sunshine and rainbows. There are some common challenges you’re likely to face along the way. But don’t worry, I’ve got some tips to help you navigate these stormy waters!
The problem: Many organizations struggle with data silos – isolated pockets of data that aren’t easily accessible or shareable across the organization.
The solution:
The challenge: With data coming from multiple sources – internal systems, third-party providers, IoT devices, and more – maintaining consistent data quality can be a Herculean task.
The approach:

The dilemma: You want to make data accessible to drive innovation and insights, but you also need to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access or breaches.
The balancing act:
The obstacle: Resistance to change and lack of understanding about the importance of data stewardship can hinder adoption across the organization.
The culture shift:
As the old saying goes, “What gets measured, gets managed.” So how do you measure the success of your data stewardship efforts? Let’s walk through some key performance indicators (KPIs) and ways to demonstrate the return on investment (ROI) of your data stewardship program.

1. Data Quality Metrics:
2. Data Governance Effectiveness:
3. Data Usage and Value:
4. Risk and Compliance:

Demonstrating the ROI of data stewardship can be challenging, as many benefits are intangible or long-term. However, here are some areas where you can quantify the impact:
1. Cost Savings:
2. Increased Revenue:
3. Improved Efficiency:
4. Risk Mitigation:
While respecting confidentiality, here are a couple of anonymized case studies that demonstrate the power of effective data stewardship:
Case Study 1: Global Financial Services Firm
Challenge: Fragmented customer data across multiple systems led to poor customer experience and missed cross-sell opportunities.
Solution: Implemented a centralized customer data platform with robust data stewardship practices.
Result: 20% increase in cross-sell revenue, 30% reduction in customer onboarding time, and 99.9% accuracy in regulatory reporting.
Case Study 2: Healthcare Provider Network
Challenge: Inconsistent patient data across hospitals led to treatment delays and potential safety risks.
Solution: Established a network-wide data stewardship program with standardized data definitions and quality processes.
Result: 50% reduction in data-related medical errors, 25% improvement in patient satisfaction scores, and $10 million annual savings in operational costs.

As I look to the future, the role of data stewards will continue to evolve. Here are some trends to watch:
Q: What is data stewardship?
A: Data stewardship is the practice of ensuring the quality, integrity, and security of an organization’s data assets throughout their lifecycle. It’s like having a dedicated guardian for your data who ensures it’s accurate, accessible, and used responsibly.
Q: What’s the difference between data governance and data stewardship?
A: Data governance sets the rules and policies for how data should be managed, while data stewardship is the hands-on implementation of these policies. Think of governance as the rulebook and stewardship as the actual playing of the game.
Q: What are the four main pillars of data stewardship?
A: The four main pillars are:
Q: What are the day-to-day responsibilities of a data steward?
A: Data stewards are responsible for:
Q: How do data stewards help with regulatory compliance?
A: They help by:
Q: What tools do data stewards typically use?
A: Key tools include:
Q: What are the biggest challenges in data stewardship?
A: The main challenges include:
As organizations continue to grapple with expanding data volumes and complex regulatory requirements, the role of data stewardship has never been more critical.
Looking ahead, the landscape of data stewardship continues to evolve. AI-augmented capabilities will transform how we monitor data quality and manage metadata. Data stewards will increasingly focus on ethical considerations in AI applications and play a crucial role in data monetization initiatives. As decentralized governance models emerge, the emphasis on data literacy will grow stronger.
The key to success lies in starting small, measuring impact, and scaling gradually. Whether you’re just beginning your data stewardship journey or looking to enhance existing programs, remember that effective data stewardship isn’t just about managing data – it’s about unlocking its full potential to drive business value while ensuring its responsible use.
By investing in data stewardship today, organizations aren’t just solving current data challenges; they’re building a foundation for data-driven success in an increasingly complex digital future. The question isn’t whether to implement data stewardship, but rather how quickly you can begin reaping its benefits.
Remember: in the world of modern business, data isn’t just an asset – it’s your competitive advantage. And data stewardship is your key to unlocking that advantage.
So, what do you think? Ready to consider data stewardship in your company?
Let me know in the comments if you liked this article. What else would you like to know about? To your success!