Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

No time to read?
Click below to listen to our podcast on Data Stewardship.
As businesses grapple with exponential data growth, with IDC predicting global data creation to reach 175 zettabytes by 2025, the role of data stewards has become more crucial than ever.
In one of my other articles, I show you how Data Stewardship fits into Data Governance and how the key components work together.
In this article, I will go deeper and explain more about the role itself. You will learn about the different types of data stewards that exist, their roles and responsibilities and what skills are needed. I will also give you a view of salaries, and even an estimate of some of the costs involved.
Whether you’re considering a career in data stewardship or looking to understand how these professionals can benefit your organization, this comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about this vital role.

A data steward is more than just a data manager – they’re the architects of an organization’s data integrity and quality. Imagine them as the quality control managers in a manufacturing plant, except instead of physical products, they oversee the lifecycle of data assets. Their role combines technical expertise with business acumen to ensure that data remains accurate, accessible, and valuable throughout its lifecycle.
All data stewards were not created equal. Well, not exactly! That’s because when you think about it you need to have more than one role. Whilst business and IT staff should be working collaboratively together, they do have different interest and therefore different responsibilities.
Business Data Stewards are usually business and data SMEs. They know how the business operates but also where the data comes from, how it is used and what it means. They should be able to direct who should have access to data and how it should be used.
Key activities include:
Technical data stewards typically work in IT. They support the business data stewards by helping them understand the underlying systems as well as supporting security requirements.
Key activities include:
Operational Data Stewards work with data relevant to their function. Under the direction of the Business Data Steward they support the management and governance of data in their area.
Key activities include:
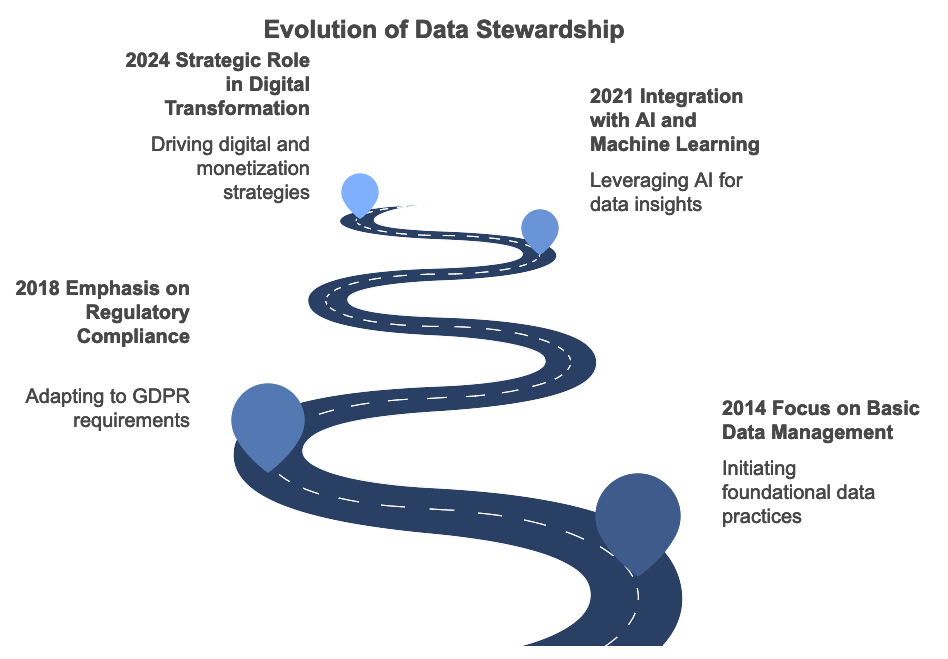
The Data Steward role has undergone significant transformation over the past decade. As you can see, the role has become more important to a point where today, a Data Steward provides critical support for digital transformation.
Modern data stewards handle a complex array of responsibilities that impact every level of an organization. Whilst not exhaustive, the following responsibilities can be considered key areas of focus.
A major bank implemented a data stewardship program that reduced data errors by 78% within six months*. Their approach included:
- Daily data quality checks
- Automated validation rules
- Weekly quality reports
- Monthly stakeholder reviews

No matter which type of data steward role you may play within your organisation, the chances are you will be using tools and technologies on a daily basis. Whilst the following doesn’t cover all of the technologies, it gives you an idea of what is used in a typical stewardship environment.
Whilst you may be savvy with the various tools you use daily, a great data steward needs to be able to communicate well. Often as a translator between business and technical staff, a data steward should understand a range of concepts, which of course, is why they have become such a valuable resource to organisations.

Ok, so like most jobs, you don’t become an expert overnight. Being a great Data Steward takes time, not only due to the technical nature of the role, but also because of the need to understand the business that you work in. The value of this combination cannot be understated.
I guarantee that if you read through and digest the blog articles on this website alone, you will be more knowledgeable than many data professionals that have been working for years!
The following gives you an idea of the types of salaries you can expect to earn as a data steward, or data governance professional. The figures are in USD*.

As we progress through 2024 and beyond, several key trends are shaping the future of data stewardship:
Whilst many companies don’t formally publicise their results, the following reflects indicative benefits that organisations can achieve through uplifting their data governance and data stewardship capabilities.
A leading hospital network implemented a data stewardship program that:
A global investment firm’s data stewardship program resulted in:
To give you an idea of how much data quality and governance technologies can costs, take a look at the following. I am currently working with a large government organisation that is implementing leading data quality and governance software.
Transitioning from on premise, licensing models to cloud based consumption models can present huge savings in both licensing and upgrade costs.

Implementing data stewardship will take time and investment, but it’s worth it. If you are able to baseline some of your core operational costs, you will see that even conservative gains will justify the costs.
Average costs for establishing a data stewardship program*:
Based on industry bench marks, organizations typically see*:
For large organisations, this equates to a lot of benefits!
Q: What’s the difference between a data steward and a data custodian?
A: A data steward focuses on the business aspects of data management and quality, while a data custodian handles the technical storage and security of data.
Q: Do I need certification to become a data steward?
A: While not always required, certifications like CDMP (Certified Data Management Professional) or DGSP (Data Governance and Stewardship Professional) can enhance your credentials.
Q: How long does it take to become a senior data steward?
A: Typically, it takes 5-7 years of experience in data management roles to reach a senior data steward position.
Q: What’s the typical size of a data stewardship team?
A: Team size varies by organization, but typically:
Q: How does data stewardship differ across industries?
A: While core principles remain the same, industries vary in:
Q: What certifications offer the best ROI for data stewards*?
A: Top certifications by market value:
As organizations continue to recognize data as a critical asset, the role of data steward has evolved from a technical position to a strategic business function. With competitive salaries, strong growth potential, and increasing demand across industries, data stewardship offers excellent career opportunities for those interested in combining technical expertise with business strategy.
Whether you’re aspiring to become a data steward or implementing data stewardship in your organization, understanding this role is crucial for modern business operations. Remember, in an age where data drives decision-making, having skilled data stewards isn’t just an advantage – it’s a necessity for business success.
Ready to take the next step? Consider exploring data stewardship certifications or evaluating how a data steward could benefit your organization. The future of data management is here, and data stewards are leading the way.
If you enjoyed this article or have any questions, please leave me a comment below. Look forward to connecting with you.
*All figures quoted are estimates at the time of writing the article, based on research. They should not be used or relied up for any formal usage. Readers must do their own research and draw their own conclusions. Thanks 🙂
Hey Data Governance Coach. There’s some good content here. Great article, thanks.